The responsive meta element
<meta name="viewport"
content="width=device-width,
initial-scale=1">
When I wrote my very first lines of
HTML and
CSS code, my immediate
priority was to (obviously) check its output on a web browser. As I
expected, that super simple document was rendered seamlessly on the
laptop. But when I've tested it on a smartphone, that same document
seemed to be somehow scaled down. The
<meta>
element above, also known as viewport meta tag, fixes that
unexpected behavior of mobile browsers.
Before explaining what it does exactly, the following two screenshots illustrate the difference between an HTML document rendered without (1st) and with (2nd) the viewport meta tag.
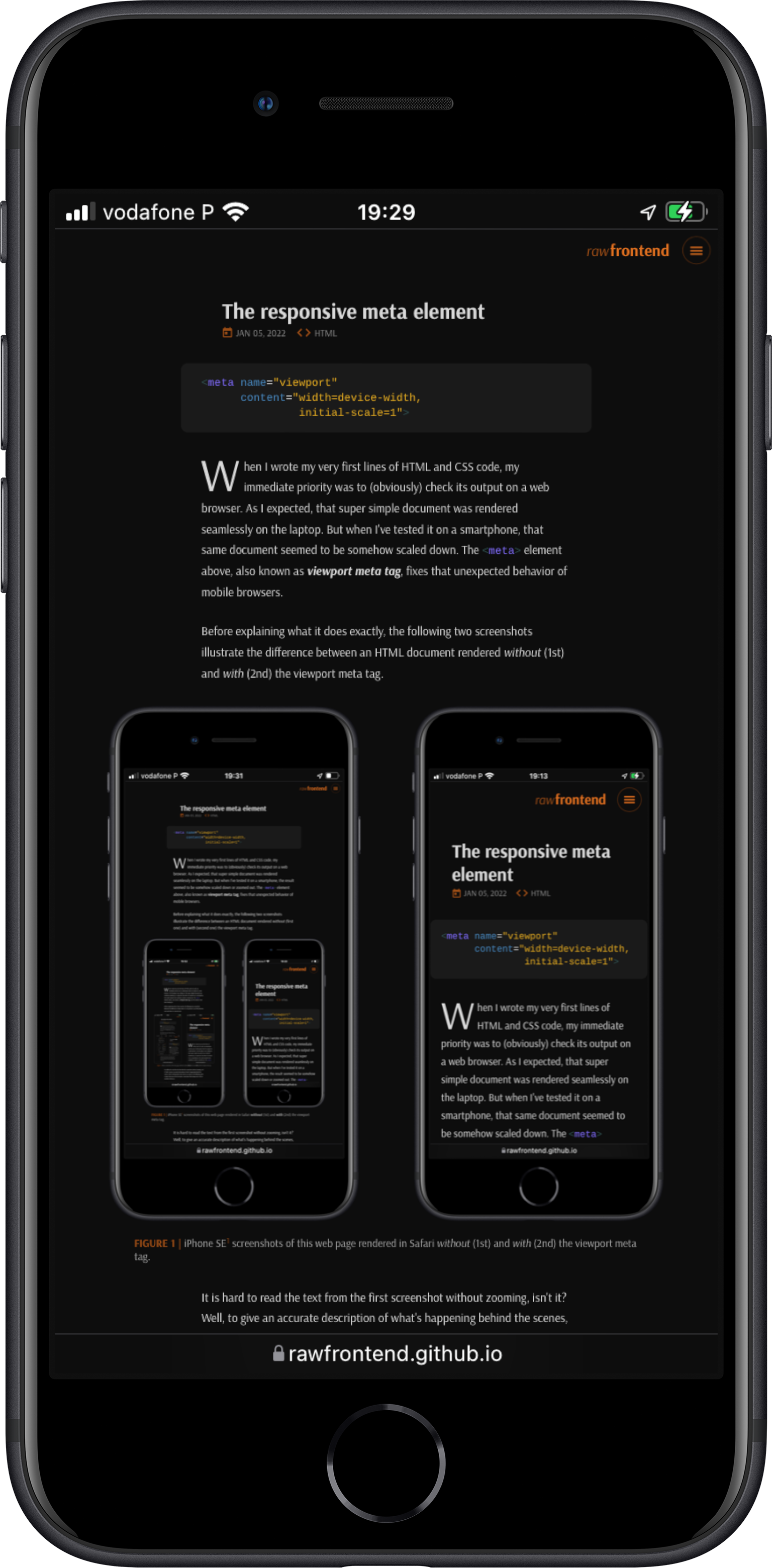

It is hard to read the text from the first screenshot without zooming, isn't it? Well, to give an accurate description of what's happening behind the scenes, there's nothing better than "listen" to an expert! (The following quote is taken from one of the first books I've read about Web Design and is still an excellent reference.)
“
To fit standard websites onto small screens, mobile browsers render the page on a canvas called the viewport and then shrink that viewport down to fit the width of the screen (device width). For example, on iPhones, mobile Safari sets the viewport width to 980 points [...], so a web page is rendered as though it were on a desktop browser window set to 980 pixels wide. That rendering gets shrunk down to the width of the screen (ranging from 320 to 414 points, depending on the iPhone model), cramming a lot of information into a tiny space.
”
So, how can the default rendering of mobile browsers be changed? Is it
possible to match the size of the viewport with the size of the device
screen? Yes, it is! It's through the already mentioned
<meta>
element, by setting the
name attribute to
viewport. It is then followed
by the content attribute,
which gets 2 values:
width=device-width —
sets the width of the viewport equal to the width of the device
screen; and initial-scale=1
— sets the zoom level to 1 (100%). This makes the rendered web
page to appear on the screen at full size
(FIGURE 1) and it allows, for example,
to test for the width with media queries. Therefore, setting
the viewport is a crucial first step in a Responsive Web Design
strategy.
Although the viewport meta tag (introduced by Apple in mobile Safari) is not part of any web standard, it is supported by most mobile browsers. For further information or technical details, check the links in the note bellow.